Hyperglycemia: What Does High Blood Sugar Feel Like?
Table of Contents
Hyperglycemia is the medical term for “high blood sugar.” Too much sugar in the blood means your body is not properly metabolizing the sugars in the foods that you eat.
Hyperglycemia or high blood sugar is most often the result of diabetes, but it can be caused by other conditions as well.
What Is Hyperglycemia?
All of the foods that we eat have some form of sugar in them. The most common sugar in foods is glucose, and it is glucose that is the primary driving agent of energy for our cells and all biological processes.
The glucose in the foods that you eat is broken down and removed from the bloodstream by insulin. In people with hyperglycemia, there is some reason why insulin is not doing an adequate job of removing glucose from the blood and into cells where it is used for energy.
The body may not be producing enough insulin, or it may not be reacting properly to the presence of insulin. Either way, too much glucose remains in the bloodstream, and hyperglycemia, or “high blood sugar,” is the result.
What Is the Difference Between Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia?
Hyperglycemia should not be confused with hypoglycemia. The two conditions may sound alike, but they could not be more different.
In medical terminology, “hyper” and “hypo” have opposite meanings. Hyperglycemia is high blood sugar or too much glucose in the blood. On the other hand, hypoglycemia is low blood sugar.
While hyperglycemia is a common symptom of diabetes, it is important to understand that both high and low blood sugar can occur even in people without diabetes. Since sugar is the essential fuel for your body, it is important to do your best to keep your blood sugar levels neither high nor low, but as close to the healthy range as possible.
Is Hyperglycemia the Same Thing as Diabetes?
Hyperglycemia usually occurs as a result of diabetes, but it is not the same thing as diabetes, because it is possible to have high blood sugar without having diabetes.
Glucose, or the amount of sugar in the blood, is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). 150 mg/dL, while eating regularly is about the normal amount. Anything above that is considered “high blood sugar” or hyperglycemia.
Diabetes is a metabolic condition that is almost always the cause of hyperglycemia, and therefore the conditions are intimately linked together, but they are not the same thing. Insulin is the hormone that is most responsible for removing glucose from the blood and transferring it into the cells where it is needed for energy.
Insulin is secreted by the pancreas. In people with diabetes, either the pancreas is not producing an adequate supply of insulin, or the body has become “resistant” to insulin. This is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
However, since insulin is produced by the pancreas, any other disease or injury that impacts the pancreas – other than diabetes – can also lead to hyperglycemia. In addition, “insulin resistance” can be caused by obesity and occur in people who are overweight and suffering from “prediabetes.” Such patients can have hyperglycemia without having full-blown diabetes yet.
In fact, it is such patients who may have high blood sugar in a prediabetes stage, that can benefit most from making dietary and lifestyle changes that may prevent both hyperglycemia and diabetes.
What are the Risk Factors for Developing Hyperglycemia
As you have probably come to realize by now, having type 1 or type 2 diabetes is the number one risk factor for developing high blood sugar, but it is not the only risk factor for hyperglycemia. Others include:
- Being overweight.
- You have a family history of diabetes.
- You are suffering from one or more of the other conditions associated with “metabolic syndrome,” such as high blood pressure, BMI in the “obese range,” or high triglycerides.
- You have polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS).
- You are of African American, Asian, Native American, or Hispanic descent.
- Having a poor diet.
- Having a sedentary lifestyle.
- Stress and anxiety.
Causes of Hyperglycemia
The main cause of hyperglycemia is almost always diabetes, that is not being controlled well either through diet or medication. However, there can be other causes of hyperglycemia.
In people with diabetes, hyperglycemia can be caused by them not taking their insulin properly or ignoring dietary and lifestyle advice. In people with diabetes, hyperglycemia can also be caused by:
- Inactivity.
- Physical stress, such as when your body is fighting illness, inflammation, or an infection.
- Emotional stress.
- Certain medications you may be taking for another condition.
In people without diabetes, hyperglycemia could be the result of:
- Other hormonal or “endocrine” conditions, such as Cushing’s disease, can lead to insulin resistance.
- Disease or injury to the pancreas.
- Prescription medications such as diuretics (water pills) or steroids.
- Surgery or trauma.
- Gestational diabetes, which can occur in pregnant women.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
It is vital that people with diabetes know the signs and symptoms of high blood sugar. In diabetics, unchecked hyperglycemia can cause a condition known as ketoacidosis, where toxins build up in the blood. This can be a very serious, even fatal, condition.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent need to urinate
- Increased hunger
- Blurry vision
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Vomiting
- Dehydration
Can Hyperglycemia be Prevented?
Again, the people at greatest risk of hyperglycemia are people with diabetes or who have “prediabetes.”
For people with diabetes, hyperglycemia can be prevented by taking your diabetes medication as instructed and following all of your doctor’s advice on diet, fitness, and exercise.
For people who have not yet developed full-blown diabetes, hyperglycemia, and indeed diabetes itself, may be prevented by:
- Eating better.
- Getting more exercise.
- Taking measures to reduce stress.
- If you do not smoke, don’t start. If you do smoke, quit.
- Reduce your consumption of alcohol.
- Taking HRT to improve metabolism.
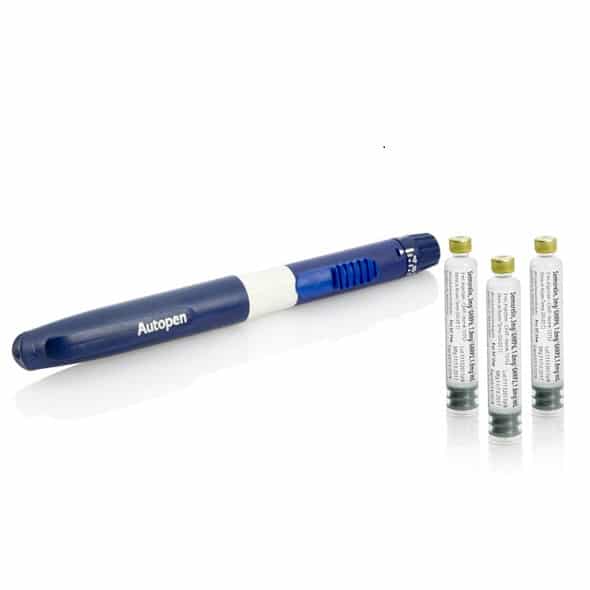

How Is Hyperglycemia Treated?
In people with diabetes, hyperglycemia is treated with insulin injections. It is important that people who have diabetes and have been prescribed insulin monitor their blood glucose levels and take the insulin exactly how they have been instructed by their healthcare provider.
In people without diabetes, particularly those who are determined to be “prediabetic,” exercise, healthier eating, and weight loss are the best ways to treat hyperglycemia.
What Happens When Hyperglycemia is Left Untreated?
Untreated hyperglycemia can have a number of negative health consequences. In people who have not yet developed diabetes, hyperglycemia left untreated can cause the development of type 2 diabetes.
In patients who already have diabetes, hyperglycemia not only can cause the emergency situation ketoacidosis – which can result in coma or death – it is largely responsible for the worst complication associated with diabetes, such as:
- Blindness
- Neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Kidney disease
- Bone and joint degradation
- Circulatory issues
- Limb loss
Conclusion
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, can be a serious condition and should never be ignored, but with proper diabetes management, and or preventative measures such as diet, HRT and exercise, it can be reduced, eliminated, or controlled.