Table of Contents
- Testosterone in Male and Female Bodies as We Age
- The Benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) For Men
- The Benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) For Women
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Testosterone Replacement Therapy
- How to Support and Enhance the Benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy Naturally
- Notes on Testosterone Safety
Testosterone, most commonly associated with masculinity and secondary sexual characteristics in men, actually has a broad range of activities in the human body that make it critical for good health in both men and women across the aging process.
The benefits of testosterone extend well beyond sexual health, although the primary male androgen (sex hormone) is certainly critical for healthy sexual function. Both men and women can experience the negative health effects of testosterone deficiency. Here, we will discuss the importance of testosterone for both men’s and women’s health across the aging process and what you can do to ensure that you have enough.
Testosterone in Male and Female Bodies as We Age
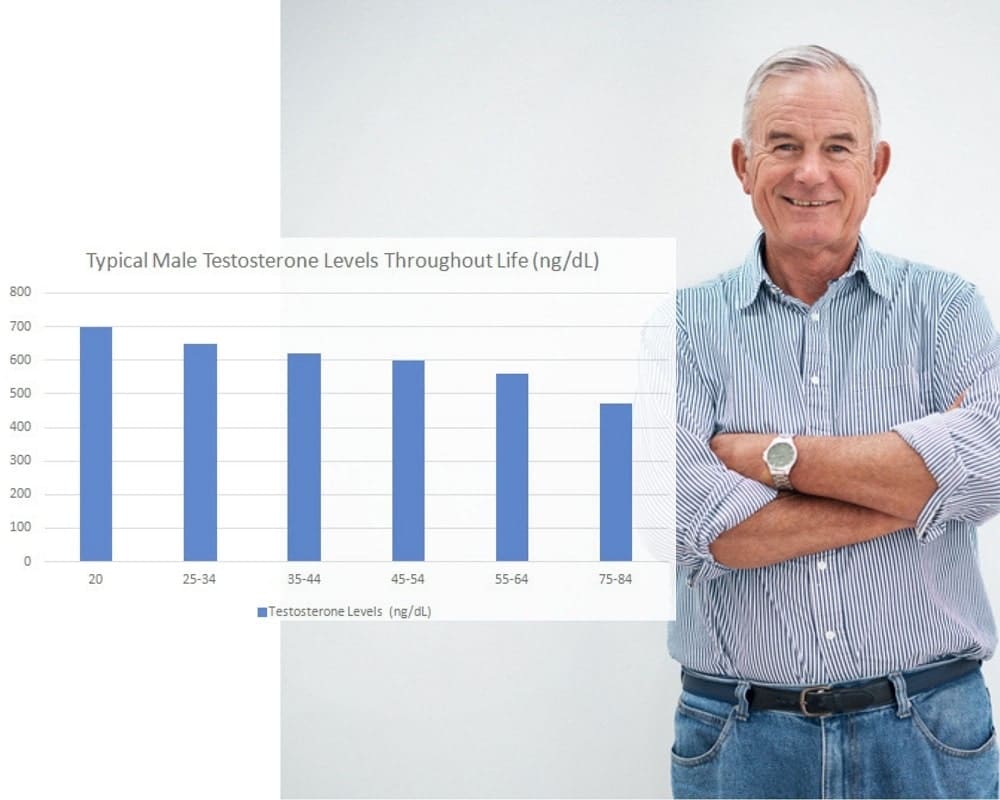
While the androgen testosterone is important for both men and women, there are important differences to discuss between the genders in terms of anti-aging medicine and how their hormonal profiles shift over time. Men generally experience a slower, steadier decline of testosterone over time. On average, the typical US male will lose about 1% of his testosterone each year after his levels reach their peak in his late teens or early 20s. The chart below illustrates the typical downward trajectory of a man’s T counts as he ages.
As you can see, it’s not uncommon for a 70-year-old male to have roughly half of the circulating testosterone as a healthy 20-year-old. For older men affected by this age-related drop in T counts, there are clinical solutions that we will discuss in a later section.
Women also require testosterone for optimal health. However, females generally have 10-20 times less circulating testosterone compared to men. In women, the adrenal glands situated above the kidneys produce most of the testosterone rather than the testes in men, which produce the bulk of testosterone found in the male body. Like men, though, women will experience a substantial drop in circulating testosterone over time. This shift occurs dramatically during the process of menopause, characterized by a permanent cessation of egg release by the ovaries and an ensuing drop in estrogen levels.
In this hormonal cascade, testosterone levels fall significantly.
Accordingly, testosterone levels affect multiple systems, tissues, organs and glands, including:
- Bone tissue
- Muscle tissue
- Prostate tissue
- Adipose tissue
- Reproductive system
- Cardiovascular system
- Immune system
- Neural system
- Hemopoietic system
The Symptoms of Low Testosterone in Men and Women
Many of the symptoms of low testosterone apply to both men and women. These include:
- Low sex drive
- Loss of muscle mass (called “sarcopenia” in the elderly)
- Emerging mental health issues such as depression and anxiety
- Chronic fatigue
- Impaired metabolism
- Unwanted weight gain
- Infertility
Osteoporosis (weakening bones)
The symptoms specifically experienced by men associated with low testosterone are:
- Inability to achieve erection (known as “erectile dysfunction” or “ED”)
- Loss of body hair
The unique symptoms that women experience due to low testosterone include:
- Vaginal dryness
- Irregular menstrual cycle (period)
- Painful intercourse
As we will explore in the next two sections, testosterone replacement therapy can help both men and women reverse the symptoms described above and recover their vitality.
The Benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) For Men
Testosterone replacement therapy, or TRT, is the medical practice of supplementing exogenous testosterone (hormones from outside the body) that replace falling levels of endogenous testosterone (the hormones produced naturally inside the body). For individuals who receive exogenous testosterone via TRT, their bodies then respond by using the exogenous testosterone as if it were the natural hormone produced in the testes in men or the adrenal glands in women.
The ease with which the body utilizes exogenous testosterone is due to the fact that the synthetic testosterone used in therapy is “bioidentical” to human-produced testosterone. This means that the synthetic testosterone you receive in therapy is molecularly identical to natural testosterone – your body can’t tell the difference.
This specific type of therapeutic approach using bioidentical hormones is called “bioidentical hormone replacement therapy,” or BHRT. The benefits of BHRT using testosterone for men with low T include:
- Lowered risk of heart attack or stroke
- Higher energy levels
- Increased bone density (i.e., preventing or delaying the development of osteoporosis)
- Greater lean muscle mass
- Restored sex drive
- Greater sperm quality/fertility
- Renewed ability to achieve erection
- Improved cognitive functioning
- Reduced or eliminated mental health symptoms
- Greater red blood cell production
- Greater immune system function
The Benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) For Women
Many of the benefits of TRT for women overlap with the benefits experienced by men while others are unique to the female sex. They are:
- Optimized cardiovascular function and decreased risk of heart attack and stroke
- Loss of unwanted body fat, especially “visceral fat” around the midsection (hips and upper thighs)
- Stronger, more resilient bones and reduced risk of osteoporosis
- Improved mood and reduced or eliminated mental health conditions associated with hormone imbalance such as anxiety and depression
- Restored libido
- Greater lubrication in the vagina during sex, resulting in more pleasurable, less painful intercourse
- Greater red blood cell production
Understandably, both male and female patients often have a number of questions before beginning therapy. Let’s explore some of the most common ones below.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Here is a sampling of the most common questions that TRT patients — both men and women — often have before beginning therapy. Of course, when you consult with your doctor prior to the start of treatment, he or she will be able to give more nuanced, individualized answers that pertain to your own case.
How Long Does It Take to Feel the Effects of Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)?
Everybody is different; your unique physiology, the severity of your testosterone deficiency, and your individual response to therapy determine when you will begin to see, feel, and experience the multiple benefits of testosterone. Also, different types of benefits take more time to appear than others, generally speaking. Below you will find a timeline detailing when the average TRT recipient begins to see specific improvements.
| Timeframe for Patients to Experience Benefits of TRT | |
| TRT Health Benefit | Timeframe Following Beginning of Therapy |
| Improved sexual libido | 3 weeks |
| Improved/harder erections (for men) and improved vaginal lubrication/more enjoyable intercourse (for women) | 6+ months |
| Improved mental health (lifted depression and anxiety, more optimistic outlook) | 3-6 weeks |
| Improved erythropoiesis (red blood cell production) | 3 months |
| Improved glycemic control (blood sugar processing) and metabolic health (lowered cholesterol levels) | 3-12 months |
| Improved body composition (greater lean muscle mass + fat loss) | 3-4 months |
Keep in mind that this is a generalized timeline for TRT benefits; your doctor, based on his or her assessment of your individual circumstances, may be able to offer a more specific timeline for accruing benefits in your own case.
What Happens When You Stop Taking Testosterone Injections?
Many patients are concerned about any negative health effects that might result from stopping testosterone injections. The majority of issues related to cessation of testosterone therapy occur when patients stop taking their medications too quickly and/or without the supervision of their doctor. The potential negative effects might include:
- Rebound depression or anxiety (especially if you experienced them before beginning TRT)
- Decreased libido
- Loss of appetite
- Irritability
- Inability to sleep (insomnia)
- Chronic fatigue
These issues associated with stopping testosterone can be mitigated or eliminated by carefully dialing down your dosage (often called “tapering”) under the guidance and supervision of your doctor. Accordingly, you should never attempt to quit taking testosterone on your own.
How Long Does It Take For Natural Testosterone to Come Back After Completing Therapy?
This is a major and understandable concern that many patients have; if I begin testosterone supplementation via TRT, what happens to my natural testosterone and when can I expect to get it back?
The answer is complicated. The body regulates its hormone production to achieve homeostasis, or, the normalized physiological environment inside the body. Accordingly, when you use exogenous testosterone to increase your levels, your body does tamp down its natural production of testosterone that normally occurs in the testes in men and the adrenal glands in women. Specifically, TRT can affect the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, a critical network of hormones and glands that includes the testes and testosterone.
Through complex signaling, this hormonal feedback loop may downregulate testosterone production in men who receive testosterone injections. The good news is that, even in extreme cases of steroid abuse, men will recover their natural ability to produce testosterone on their own. The process may take several weeks to several months, depending on individual factors.
In the next section, we will explore ways that you can naturally increase your circulating testosterone levels at any age or health status. Quick, affordable, and simple lab tests can determine your testosterone levels. Your doctor will likely order regular, ongoing testing to monitor your progress and make sure that you stay on the right track in terms of restoring your testosterone levels.
How Do You Feel After Taking Testosterone?
The men and women with diagnosed testosterone deficiencies who receive TRT report the following benefits in terms of how they feel:
- More confidence
- Less anxiety
- Greater energy (some men and women describe their energy levels as “limitless” after completing therapy)
- Renewed interest in sex
- Rekindled romance
- Feeling younger and more vibrant
- A rediscovered “lust for life”
- Improved physical performance, including cardiovascular endurance and greater strength
- Less joint pain
The reviews from real-life patients who have experienced near-miraculous health turnarounds are legion: “Since starting testosterone replacement therapy, I have no more depression, laugh more, enjoy socializing, and feel better than I have in years.”
Dr. Stefaan Vossen, himself a doctor who suffered from the effects of low testosterone and found recovery through TRT, says:
“A drop in men’s vitality is brushed under the carpet in our society as an inevitable part of ageing. But from my experience, men don’t have to accept the loss of their vitality. They can do something about it.”
If you’ve gone to your primary care doctor with complaints of low energy, loss of muscle mass, low libido, or increasing depression or anxiety but received no answers, there is hope for recovery. It’s very likely, especially if you are over 40, that what you are experiencing are the classic signs of testosterone deficiency.
How to Support and Enhance the Benefits of Testosterone Replacement Therapy Naturally
Effectively elevating your testosterone levels doesn’t start and stop at the clinic; to truly make your testosterone gains sustainable, you also must make permanent changes to your lifestyle. Science has a lot to say in terms of how to sustainably elevate T counts and keep them high throughout the aging process. The proven methods to improve testosterone levels are:
- Eating an optimal diet. This means eliminating processed, pre-packaged foods such as chips, sodas, candies, etc. from your diet and focusing on whole foods that promote a healthy hormonal profile, including stimulating maximum testosterone production. The best foods for improving testosterone counts include fish (especially shellfish rich in zinc such as oysters), lean meats, cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale, spinach, etc.), eggs, avocados, and ginger. Anti-testosterone food items to limit or avoid altogether include soy, dairy, alcohol, and mint.
- Supplement as necessary. There is solid clinical evidence that a variety of supplements can effectively elevate testosterone levels in deficient men and women. These include zinc, certain amino acids like D-aspartic acid, ancient ayurvedic medicinal tool ashwagandha, vitamin D (actually a steroid hormone and not a vitamin), and fenugreek.
- Lift weights. Hitting the gym at least a few times per week is arguably the best regular discipline that you can incorporate into your daily routine to boost your testosterone levels. While all forms of exercise may be beneficial for testosterone levels, strength training with weights is the most well-documented for producing maximum testosterone gains in both men and women.
- Practice mindfulness. The so-called “stress hormone” cortisol is a natural testosterone killer. Unfortunately, due to the everyday stresses of the modern lifestyle, many of us carry around excessive amounts of cortisol in our blood, sapping our testosterone supply and greatly limiting our quality of life.
You can smash cortisol by engaging in what are called “mindfulness practices.” These include meditation, yoga, and controlled breathing.
- Get plenty of restful sleep. When it comes to optimizing all hormone levels, testosterone included, sleep is critically important. The average human adult needs at least 7-9 hours of full, restful sleep each night. The evidence is clear; individuals who fall short of the 7-9-hour sleep requirement have significantly lower testosterone levels than those who get adequate rest. In fact, one study found that those who sleep 5 hours or less per night have, on average, 15% less testosterone than their well-rested peers.
- Avoid contaminants in the environment that mimic estrogen. Recently, in an effort to understand rapidly declining testosterone levels among men in the West, scientists have begun to pay more attention to environmental factors that might be driving hormonal issues in the population. For example, bisphenol A, or BPA, a common additive to plastics that can be absorbed into the bloodstream through the skin, mimics estrogen and drives testosterone counts lower. This is just the tip of the iceberg; other toxins in the environment known to have detrimental impacts on testosterone levels include herbicides and pesticides used on crops, parabens in shampoos and cosmetics, and chemicals in cookware. All of these materials can lower T counts. Talk to your doctor about the best ways to limit your exposure to these materials and avoid the negative impacts on your hormones.
Notes on Testosterone Safety
Never purchase your testosterone from an unlicensed pharmacy. In addition to purchasing testosterone without a prescription being illegal, you also gamble with your health and safety when you look to the black or gray market for testosterone supplies.
Studies by the World Health Organization (WHO), the premier international medical authority, have estimated that 1 in 10 medical supplies from the Third World are either “falsified” or “substandard.”
This means that the medications imported from these countries – which do not have the same regulatory standards or oversight that pharmaceutical manufacturers in the US and Europe do – are likely to either a.) contain added harmful ingredients that are not labeled or b.) not contain the medications that they claim to – in this case, high-quality synthetic testosterone.
Avoid these issues by always looking for the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) seal of approval on testosterone supplements that you use. Your doctor will also be familiar with the T products licensed and approved for therapeutic use in the US.




No Comments
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.