Can Low Testosterone Lead to Gynecomastia?
Table of Contents
This article discusses the role that testosterone plays in the body, regulating tissue deposits. Many patients who are interested in boosting their health through hormone replacement therapy (HRT) have questions about testosterone and gynecomastia, the condition of unwanted breast tissue growth.
Let’s explore the complex relationship between gynecomastia and the endocrine (hormone) system and the latest healthcare developments for treating the condition.
What is Gynecomastia?
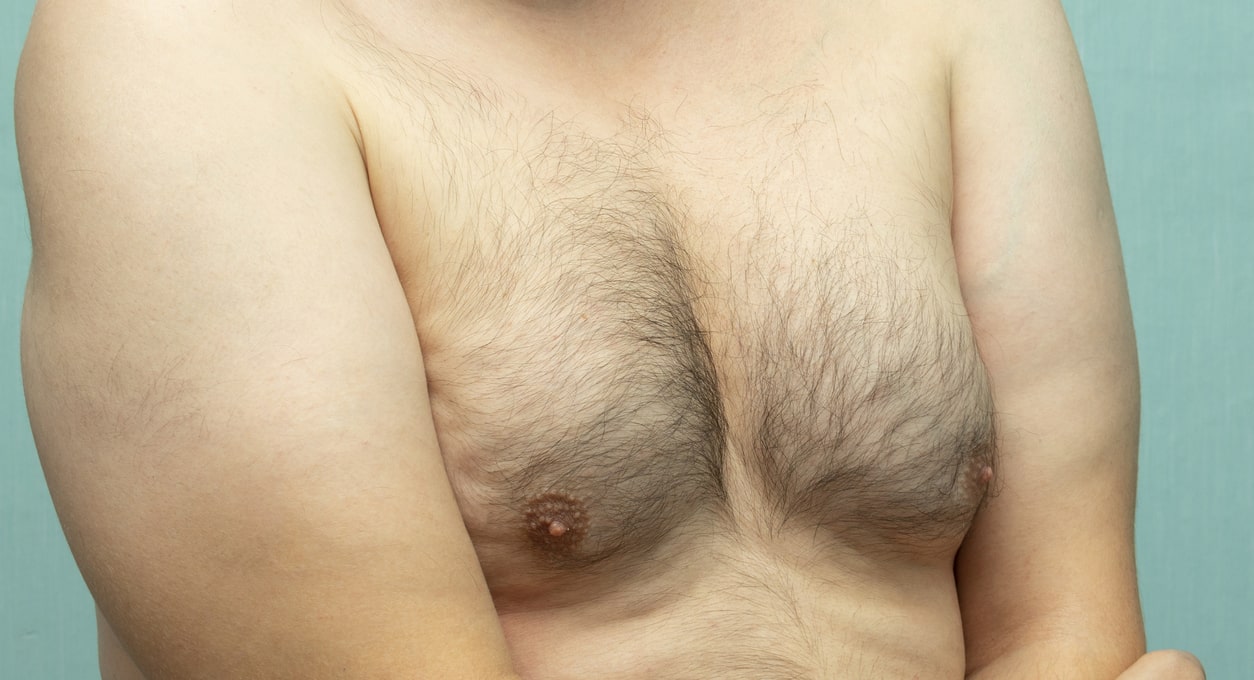
Gynecomastia is the medical term for the abnormal growth of tissue in the breasts of men or boys. In humans, females typically grow breast tissue as a normal part of puberty for reproductive purposes. Men’s’ or boys’ breast tissue mass does not increase during puberty. If gynecomastia does develop, it may be a sign of a more serious health condition.
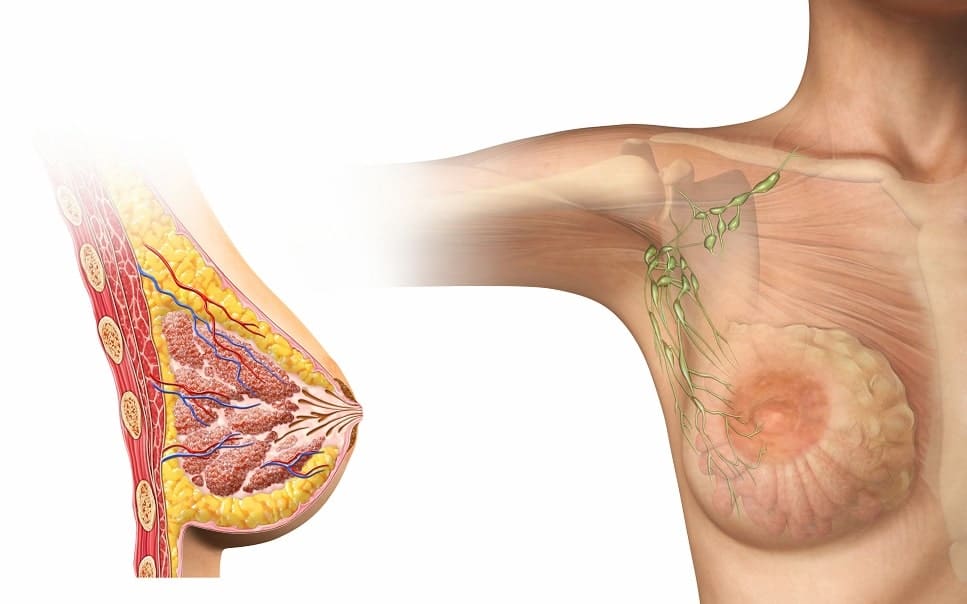
In both men and women, the breasts contain mammary glands. These glands begin to produce milk when a woman gives birth that is essential for the survival of her baby.
The human hormone system is a complex web of chemical messengers that signal important activities throughout the body. In women, the following hormones work in concert to spur breast tissue growth during female puberty:
- Estrogen.
- Progesterone.
- Human Growth Hormone (GH).
- Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1).
- Prolactin.
Hormonal deficiencies in women can sometimes lead to unusual breast tissue growth. For example, researchers are interested in the link between higher male sex hormones called androgens (including testosterone) and pathological breast tissue growth. This illustration shows what breast tissue in post-adolescent women normally looks like:
Unlike women, men normally do not develop breast tissue.
What Causes Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia occurs when the delicate balance between testosterone and estrogen levels in the body is disrupted. All the hormones of the endocrine system exist in ratio to one another, so a change from normal levels can trigger many health problems, including gynecomastia.
The condition is frequently seen, for example, in bodybuilders who utilize illegal steroids to increase their gym performance and add lean muscle mass. The uncontrolled spike in testosterone upsets its balance with estrogen, leading to the development of breast tissue.
What Medications Cause Gynecomastia?
Several prescription and over-the-counter drugs commonly taken in the US are proven to contribute to the development of male breast tissue. They are:
- Anti-androgens. This class of drugs is used to treat enlarged prostate in men because of the link between prostate function and testosterone Examples of these drugs include Proscar, Propecia, Aldactone, and Carospir.
- Antibiotics. Drugs that target harmful bacteria can
- Calcium channel blockers. These medications are typically prescribed to patients with certain heart conditions.
- Steroids. Illegally-sourced androgens in the form of steroids have long been associated with gynecomastia.
If you are prescribed any of these drugs, consult with your doctor before discontinuing use to avoid any risks that might be associated with stopping them.
Is Gynecomastia Dangerous?
Occasionally, gynecomastia can occur briefly in newborn babies, adolescent boys, and older men because of shifting hormone levels. Such cases are normal and usually harmless when they resolve themselves.
In rare cases, gynecomastia can be dangerous – for example, the small but important risk of cancer.
Does Gynecomastia Cause Cancer?
The chances of men developing cancer due to gynecomastia is small. Only about 1% of patients who present with gynecomastia wind up battling breast cancer. In the vast majority of cases, the breast tissue growth caused by the condition is considered “benign,” meaning that it is not cancerous.
Male breast tissue growth typically occurs in the three stages of life we discussed earlier. In many instances, it is normal and natural. Below we’ll discuss each stage of human life in which gynecomastia commonly occurs:
- Infant Gynecomastia. Human infancy is called the neonatal stage of human development. Gynecomastia appears during this period when babies receive large amounts of estrogen through their mother’s breast milk. The vast majority of infant gynecomastia cases are not serious and resolve on their own.
- Adolescent Gynecomastia. At least half of all boys develop some amount of breast tissue as they enter puberty because of the massive internal changes to hormones during this period of transition from childhood to adulthood. In most cases, the tissue subsides over a period of a few years.
- Adult Gynecomastia. As many as one out of every four men (25%) develops gynecomastia past the age of 50 due to falling testosterone levels that upset the balance between male and female sex hormones described earlier. Lifestyle adjustments and testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can treat adult gynecomastia.
We’ll discuss TRT in more detail later.
Symptoms of Gynecomastia
The symptoms of gynecomastia include:
- Breast pain.
- Nipple discharge in one or both breasts.
- Swollen breast tissue.
- Breast tenderness.
Bilateral vs. Asymmetrical Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia presents either as bilateral or asymmetrical. In instances of bilateral gynecomastia, the abnormal tissue growth is evenly distributed between both breasts. On the other hand, asymmetrical gynecomastia refers to cases where tissue growth occurs in only one breast or is distributed unevenly between the two.
How Is Low Testosterone Related to Gynecomastia in Adult Men?
11% of adult male gynecomastia cases are caused by hypogonadism, the medical term for the improper functioning of testicles. In humans and all mammals, the testicles are the primary producer of testosterone that the body needs to function optimally.
How Are Testosterone Levels Measured?
When your doctor suspects that low testosterone might be causing gynecomastia, he or she will order a blood test. It is a quick and easy blood draw that is sent to a lab for testing. The test will measure “free” testosterone in the blood – meaning the testosterone that is available for use throughout the body. About 98% of testosterone is considered “locked” because it is bound to other molecules.
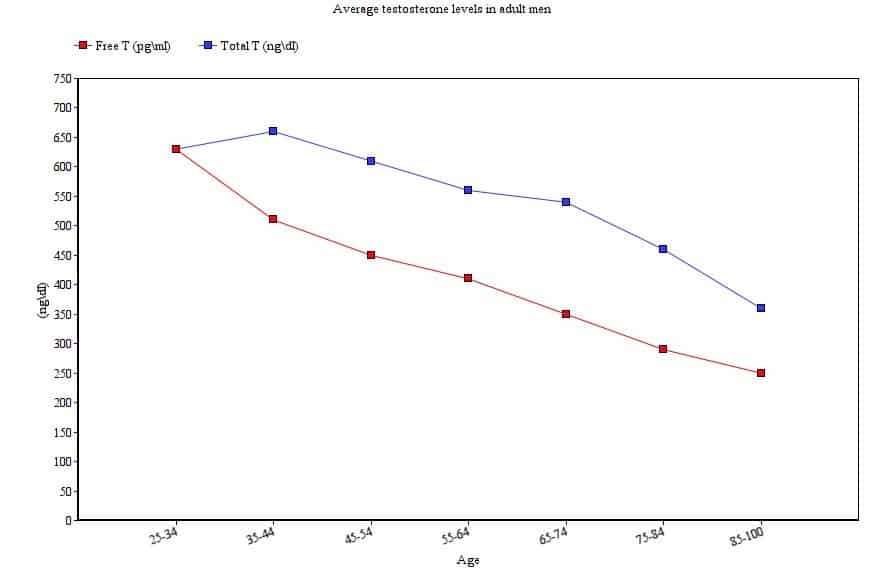
The industry standard for testosterone testing utilizes nanograms per deciliter (ng/dl) as the measurement of T levels in the blood. This chart shows the average testosterone levels in men as they move through life:
Notice the gradual decline of both free and total testosterone levels as men age. Although declining T levels are typical, they are not fixed. Through supplementation, which we’ll discuss further below, optimal T levels can be restored.
Treatment of Low T and Gynecomastia
Because many men experience low T symptoms and gynecomastia concurrently, separate approaches are required to treat each respective condition.
Treating Low T in Older Men
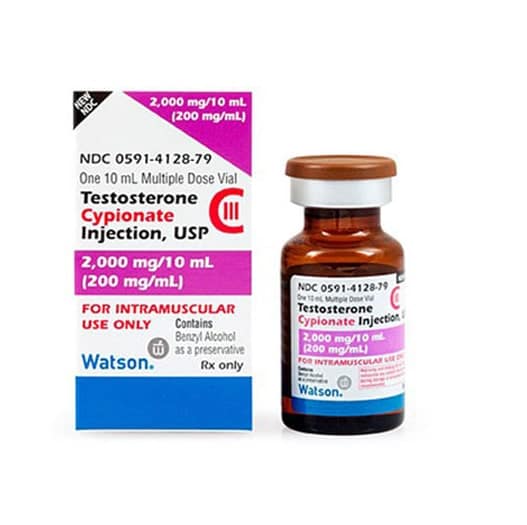
Testosterone deficiencies are increasingly common among older men. Our sedentary lifestyles, poor eating habits, and lack of adequate sleep all contribute to the growing public health problem. In fact, as many as 1 in 4 men over 45 will develop symptoms of low T. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) involves the clinical introduction of exogenous (sourced from outside the body) testosterone, usually in the form of a series of therapeutic injections over a period of weeks or months.
Choosing an experienced, licensed medical provider is crucial to protect your health. In a clinical setting, the doctor will monitor your body’s increasing testosterone levels and look out for any negative side effects. The appropriate provision of TRT requires vigilance from the provider. The dosages of testosterone should be carefully titrated to achieve optimal levels. Too much testosterone can cause adverse reactions.
Restoring T levels to a healthy range will usually prevent further unwanted breast development. However, specific treatments for gynecomastia exist as well. Many patients who present with both low T and breast tissue growth opt for simultaneous treatment of both related conditions.
Treating Gynecomastia
Although gynecomastia is usually harmless health-wise, many men are understandably self-conscious about enlarged breasts. Several medications are approved to treat the condition, including:
- raloxifene (Evista)
- tamoxifen (Soltamox)
Also, many men opt for liposuction, the surgical removal of fatty tissue deposits in the breast.
How to Prevent Gynecomastia
As the saying goes, “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” This piece of folk wisdom works for gynecomastia. Maintaining the proper balance of hormones in your body is essential for preventing unwanted breast tissue growth and a host of other conditions that can threaten your health and decrease your quality of life.
- For better hormonal health, incorporate the following changes into your life:
- Optimal Diet.
- Medication monitoring. The medications that we.
- Proper Sleep. Adults need at least 7 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to maintain normal endocrine function. The majority of Americans do not get enough sleep.
- Regular exercise. A solid workout regimen, especially one including lots of anabolic exertion like weightlifting, is a surefire way to improve your hormonal profile.
- Stress reduction. Countless effective methods for relaxation exist. Many people find enormous benefit from meditation and breathing exercises. In addition, sleep and exercises naturally alleviate stress and induce relaxation with the release of “feel-good” hormones called endorphins.
The Bottom Line on Gynecomastia and Testosterone
Gynecomastia frequently results from falling testosterone levels. As many as 25% of men over the age of 40 will experience gynecomastia in varying degrees of severity.
Through testosterone replacement therapy, patients can restore healthy levels of the hormone, correcting the imbalance between testosterone and estrogen which is the underlying cause of gynecomastia in men. If you a man over 40, you are at risk of developing low T and the conditions that result from hormonal imbalances in the body such as gynecomastia.
Give MedZone a call today to get in touch with an experienced hormone doctor who can diagnose any deficiencies. If you have a testosterone deficit, we will explore your treatment options together to come up with the best plan to reclaim your male vitality, boost energy levels, and recover your overall good health.