The Connection Between Testosterone, Sperm Production, and Fertility
Table of Contents
- What Factors Affect Male Fertility and How Is It Measured in Men?
- Infertility in Men: An American Epidemic
- How Testosterone Promotes Sperm Production
- How Different Testosterone Levels Affect Sperm Count
- How Testosterone Replacement Can Impact Sperm Count
- The Bottom Line on Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Fertility
More than any other hormone, testosterone levels in the blood have a direct and proven effect on sperm counts. Unfortunately, testosterone levels have declined precipitously among American men. Inactive lifestyles, an ongoing obesity epidemic, smoking, and, above all, poor diet all play roles in reducing testosterone levels, even in relatively young and healthy men. Many who have low testosterone (low T) are not aware of their condition or how it might affect their futures.
As we’ll show in this article, testosterone and sperm counts are inextricably linked. Replacing testosterone with appropriate therapy could significantly enhance a male’s fertility as his sperm production rebounds.
What Factors Affect Male Fertility and How Is It Measured in Men?
“Fertility” refers to the ability of a man to successfully impregnate a woman through intercourse by fertilizing an egg. The primary measures of fertility are overall sperm count and, just as importantly, the capability to move through the woman’s ovaries to reach the egg. This is called sperm “motility.”
Male fertility can be assessed with the following medical tests:
- General physical examination and medical history.
- Testicular biopsy.
- Hormone testing.
- Post-ejaculation urinalysis.
- Genetic tests
- Transrectal ultrasound.
- Semen analysis.
- Scrotal ultrasound.
- Specialized sperm function tests.
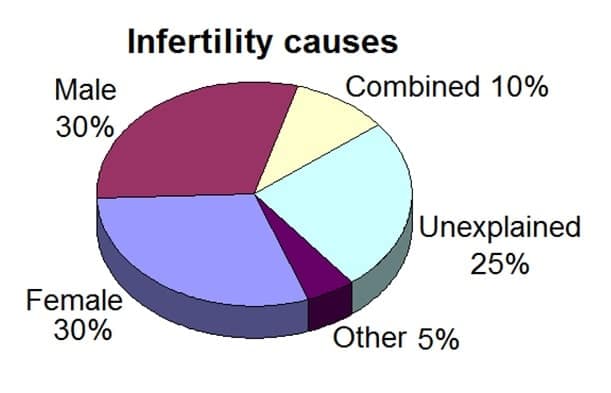
According to one study, “semen abnormalities”, which are often caused by hormonal imbalances, are significant factors in 44% of cases where couples attempt to conceive but cannot due to male infertility.
Among couples attempting to start a family, women often bear the brunt of overcoming obstacles to getting pregnant. However, in a large percentage of cases, the man is actually the cause. This chart breaks down the causes of infertility:
Infertility in Men: An American Epidemic
Men in the United States, as well as men across the West from Europe to Australia, have seen a precipitous decline in sperm counts in recent decades. The trend has alarmed doctors and scientists who see the long-term impacts of a society that is unable to healthily reproduce. The falling sperm counts of men is one of the major contributing factors to the slowing rates of reproduction observed throughout advanced societies.
In the United States, women have fewer babies than ever before. The reasons that women have fewer pregnancies than in generations past are complex, but it is partially due to men’s low sperm count.
Why Sperm Counts Matter
On a macro scale, “fertility rate” is a statistical measure of how many children women have. At the societal level, fertility rates can be used to predict future population growth. The US, with a 1.77 fertility rate, means that women have fewer than 2 babies each – not enough to keep the population steady. The 2-baby threshold is called the “replacement level” by public health officials. Any fertility rate under 2 signals potential trouble on the horizon.
Low sperm counts have profound effects on a man’s personal life as well. Low sperm count and/or low quality of sperm can be a major burden for men and their partners who hope to start a family. Even otherwise healthy couples with plans for children often struggle to achieve pregnancy. Again, the causes for an inability to become pregnant vary, but sperm count is a common factor. Here’s how sperm affects fertility.
How Sperm Count Affects Fertility
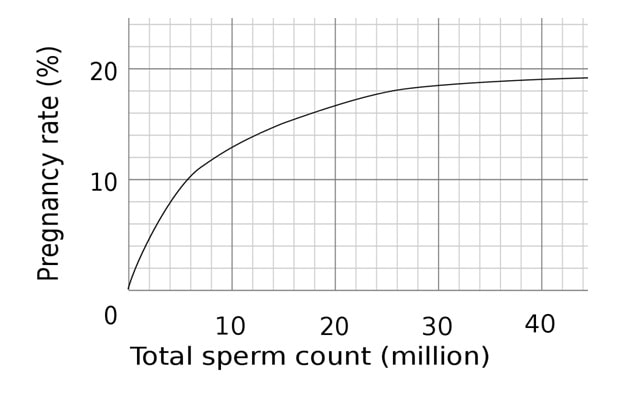
Boosting sperm counts — through testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), which we’ll discuss later, as well as through lifestyle changes – is a proven strategy to increase the chances of successful fertilization of an egg and a resulting pregnancy. As the graph below demonstrates, the total sperm count is closely linked to pregnancy rates. As the numbers of sperm increase, so does the likelihood of pregnancy.
Any man who has struggled to impregnate his partner should consider being tested both for low sperm count and for low testosterone. As we’ll explore later, the two conditions often go hand-in-hand.
How Testosterone Promotes Sperm Production
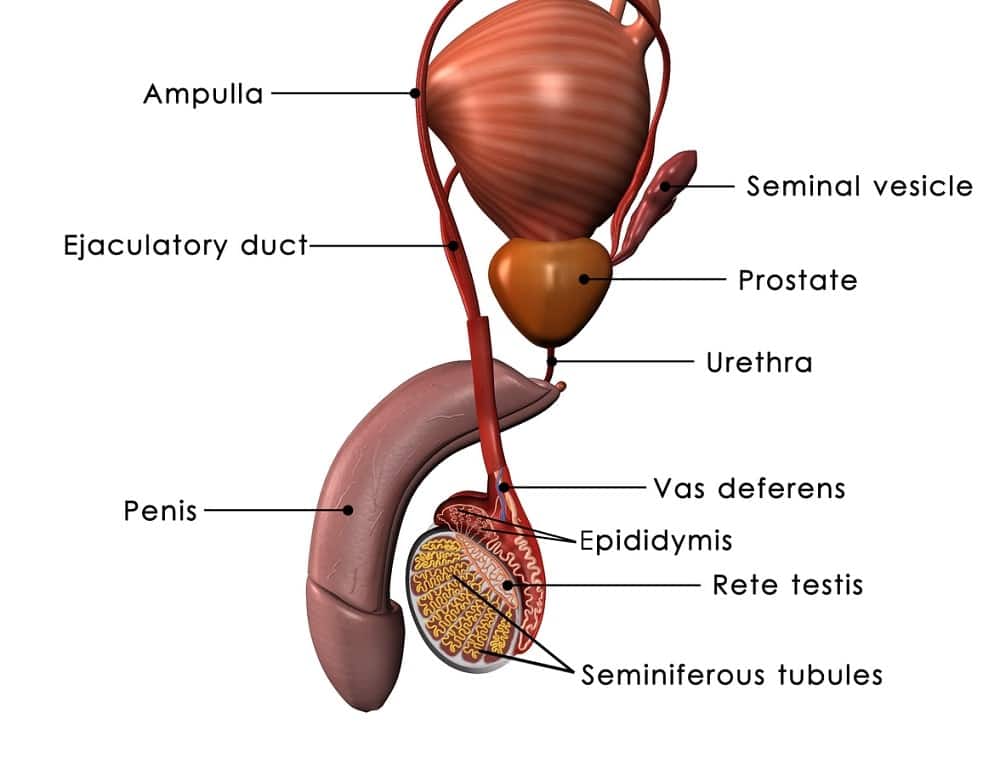
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone, playing a crucial role in reproduction. Testosterone is produced in the male testes, the same glands in the body where sperm is manufactured. Medical literature describes sperm production as “hormonally driven,” meaning that the body requires the proper signaling from testosterone, working in tandem with other hormones, to catalyze sperm production.
Other than testosterone, the other two hormones that direct sperm production are called luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
In the medical literature, “spermatogenesis” refers to the process of sperm production. Scientists have recently uncovered a deeper understanding of how spermatogenesis works and why it depends so heavily on testosterone.
Testosterone is intricately involved in spermatogenesis from start to finish. Without proper levels of testosterone in circulation, sperm production is severely limited. This is one of the major reasons that older men who are planning for families often struggle to impregnate their partners.
How Different Testosterone Levels Affect Sperm Count
While low testosterone levels are frequently the cause of infertility in men, higher than normal testosterone levels can also make conception a challenge. Through therapy, doctors carefully titrate the dosage that patients receive to arrive at the “sweet spot” of ideal testosterone levels.
Here is how varying levels of testosterone can affect sperm count:
- Low testosterone. Testosterone is present in the testes at much higher rates than in the blood. Therefore, low testosterone counts in the blood may not always indicate a low sperm count. Sometimes, though, low testosterone can severely limit sperm production. In addition to exerting a direct negative effect on sperm production, low testosterone levels also decrease sex drive in men and contribute to erectile dysfunction (inability to achieve or maintain an erection), creating further barriers to conception.
- High testosterone. Medical researchers describe the relationship between testosterone and sperm production as a “feedback loop”. Uncontrolled increases in testosterone – such as through unsupervised, illegal steroid use – signals to the pituitary gland in the brain to inhibit the production of FSH and LH, the other crucial hormones to spermatogenesis that we discussed earlier. When higher than normal testosterone levels are detected in the blood, specialized Sertoli cells signal for the slowdown of FSH and LH release, thereby limiting sperm production. This is called a “negative feedback loop.”
- Healthy Testosterone Levels. In men with healthy testosterone levels, FSH and LH are present at normal levels. Sperm production carries on at a normal rate, improving fertility and the chances of conception for men planning families.
The need to strike the delicate balance between LH, FSH, and testosterone, as well as all hormones in the body, illustrates the importance of proper medical supervision during testosterone supplementation.
Professional TRT providers understand the intricate interactions between the various hormones involved in fertility and account for these interactions when developing the optimal treatment plan for each patient.
How Testosterone Replacement Can Impact Sperm Count
Modern medicine has a greater understanding than ever of how testosterone works in the body and how it impacts reproductive health in men.
Can Testosterone Replacement Therapy Decrease Sperm Count?
TRT has its advantages and disadvantages. While it helps restore youthful vitality, a renewed vigor for life, and recaptured physical strength lost from years of declining testosterone, TRT can also trigger decreased sperm production in some instances.
Can Testosterone Replacement Therapy Increase Sperm Count?
As we discussed earlier, testosterone levels in the testicles are independent of testosterone circulating in the blood – meaning that a man can experience a deficit of testosterone throughout his body but still maintain enough where it counts to produce healthy amounts of sperm.
Although TRT is not recommended as a treatment for infertility, it does improve fertility indirectly by increasing sex drive and potentially treating erectile dysfunction. For men who struggle to achieve erections, performance anxiety can significantly reduce the enjoyment of sex. When men recover their ability to perform and become more confident in the bedroom, many report higher levels of sexual satisfaction within their relationships.
What Consequences Does TRT Have for Male Fertility?
Due to the “negative feedback loop” described earlier, there is a risk of reduced fertility as a result of TRT. For men who experience drop-offs in sperm production due to TRT, several therapeutic remedies can effectively restore spermatogenesis and improve fertility.
The Bottom Line on Testosterone Replacement Therapy and Fertility
If you are a man interested in feeling younger and more vibrant through TRT, you can mitigate the risks of infertility by enlisting the services of a qualified, experienced professional who understands the complex interactions between testosterone and sperm production.
Understandably, replacing testosterone through therapeutic supplementation is a big decision with potential long-lasting impacts, both positive and negative. When you visit our clinic, our friendly doctors will take the time to go over the risks and rewards associated with TRT as well as to analyze a patient’s risk factors. Then, we work together in order to develop a treatment plan that delivers the maximum benefit (restored testosterone levels) with the smallest risk of unwanted side effects possible.