Which HGH Supplements Work and Which Don’t: Fact or Fiction Review
Table of Contents
For patients who experience a deficiency of the crucial human growth hormone (HGH) – one of the hundreds of hormones needed to carry out daily biological functions – relief often arrives in the form of exogenous, synthetic growth hormone. With careful dose titration, these synthetic substitute hormones serve as a viable replacement option to safely restore HGH to optimal levels in patients with suboptimal blood plasma concentrations.
As a patient new to the world of hormone replacement therapy (HRT), your choices can seem overwhelming. You have a range of options, both in terms of manufacturers and type of HGH supplement. Growth Hormone products come packaged as gels, patches, pills, powders, and more.
In this article, we’ll explore how HGH supplements work. We will separate the high-quality, potent, effective GH products on the market from the pretenders. Finally, we’ll discuss strategies to source clean HGH supplements from reputable manufacturers.
How Do HGH Supplements Work?
Human Growth Hormone supplementation is designed to act as an effective substitute for endogenous HGH when it exists in inadequate supply in the blood. The Growth Hormone introduced through supplementation mimics the activity of the naturally-occurring HGH that the liver normally produces.
With so many choices of HGH supplements, knowing which ones work and which ones don't will save you money and, ultimately, could save your health.
Various delivery systems exist to seed exogenous HGH supplements in the body so the synthetic hormone can go to work. The most common methods of HGH supplementation, along with their associated advantages and disadvantages, are below.
- Gels. Studies on topical solutions containing 15% HGH show that patients experience beneficial upticks in plasma HGH concentrations with this treatment method. However, over time, patient responses to gels often decline, necessitating alternative treatment modalities.
- Patches. A skin patch, called a “transdermal patch” in the medical community, is one of the most convenient options for hormone replacement therapy – no mess to clean up and no preparation required. Many HGH patches on the market today utilize “microneedle” technology to deliver Growth Hormone subcutaneously through microscopic needles. This promising avenue of technological progress could be the future of hormone replacement therapy.
- Pills. Researchers have looked into the potential application of amino acid supplements administered orally to boost GH levels in healthy adults.
However, the results have been mixed. More research is needed before HGH supplementation in pill form becomes a viable treatment method. - Powders. Because they are typically comprised of the same ingredients, the same analysis of HGH pills applies to HGH powders.
Until drug producers conduct more research and/or innovate new oral formulations, patients should remain wary of orally-administered of HGH treatments. - Injectable HGH. Human Growth Hormone therapy via injection is the “gold standard” of supplementation. Injectable HGH has been clinically demonstrated time and time again to safely elevate HGH plasma concentrations to normal levels in otherwise healthy patients.

The Bottom Line on GH Therapy Methods
Although other methods like patches or gels are often good complementary treatment modalities, injection is still king in terms of its track record of effectiveness, safety, and predictability of success. In many cases, doctors might include multiple delivery routes for Growth Hormone administration. For example, to lower the frequency of necessary injections, a patch or gel might be used to amplify the effects of injected HGH.
As a general rule, you should avoid oral administration (i.e., pills and powders) due to a current lack of evidence for efficacy. Treatment methods vary depending on individual circumstances and the preferences of the patient.
Are HGH Supplements Really Effective? What the Research Says
Naturally, many people remain skeptical of the field of HRT – and for good reason. The HRT field is relatively new, and there is still much to learn about how hormone supplementation should be performed, who is a good candidate to receive it, and the long-term effectiveness of treatment to restore hormone levels.
Due to the complex interactions between the hormone, immune, and nervous systems, predicting how an individual patient will respond to Growth Hormone therapy is difficult. Risk analysis must be conducted on a case-by-case basis.
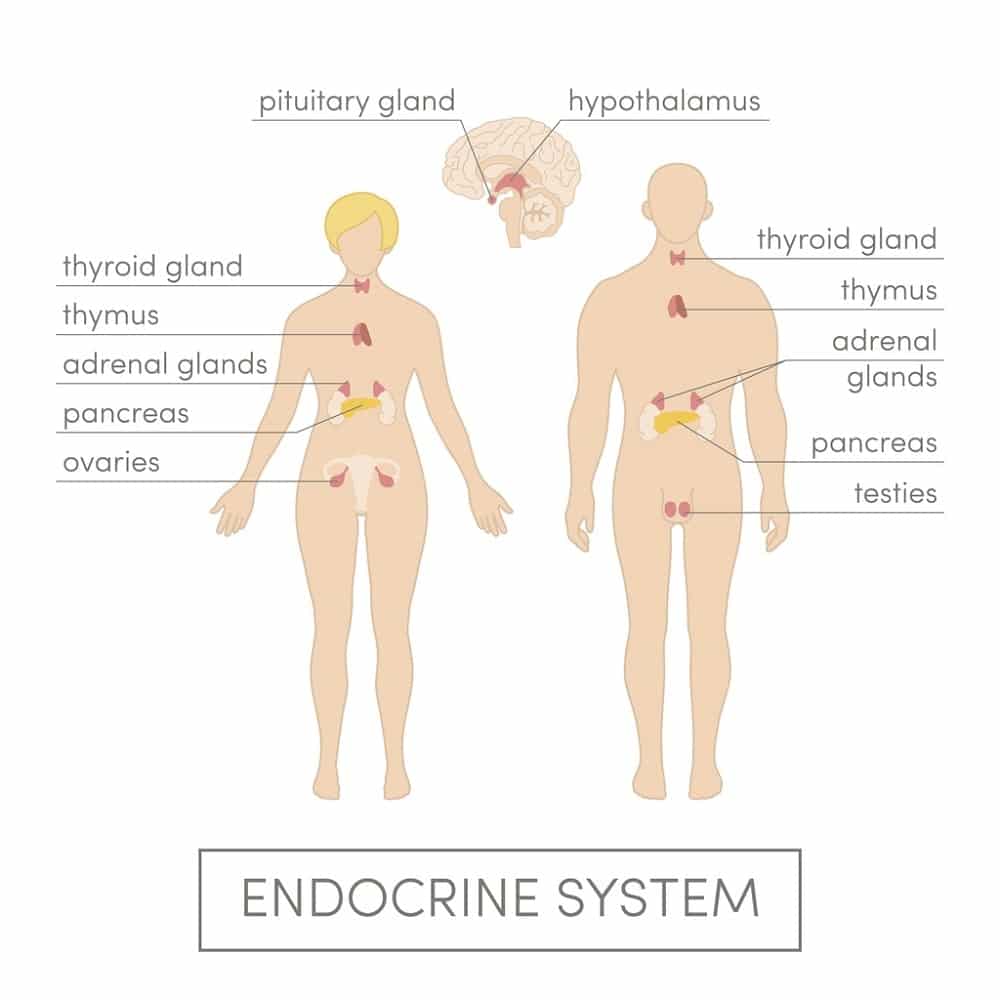
The human endocrine system – as it extensively interfaces with the nervous and immune systems — is incredibly complex in vivo in terms of its role in regulating numerous biological activities at the molecular level. The medical community has only begun to unravel the complex signaling web of the endocrine system and its implications for advancing human health.
However, despite the knowledge gaps, the existing scientific literature does tell us a lot about HGH supplementation and how it works. Here is what the data says.
Does HGH Really Restore Human Growth Hormone Levels?
The evidence that GH really restores human growth hormone levels is overwhelming. Advances in testing in recent decades have afforded researchers the means to accurately measure the effects of HGH supplementation that previously did not exist. As a result, we have reams of data to document the effectiveness of HGH supplements for restoring Human Growth Hormone levels in patients impacted by deficiencies.
Is HGH Supplementation Really the Most Effective Way to Elevate Levels HGH in the Body?
Depending on the situation, yes. Exhaustive reviews of the available literatureindicate that Growth Hormone supplements are reliably effective at yielding positive results for adults with deficiencies. Studies consistently show positive responses in blood profiles with a minimal risk of side effects among the general public. However, these findings come with strings attached.
Primary vs. Secondary Symptoms of HGH Deficiency
HGH deficiency as a symptom of a hormone imbalance may be either a primary symptom (the liver is not producing adequate supplies of HGH) or a secondary symptom of another underlying condition. Therefore, treatment protocols vary depending on the source of the dysfunction. In some cases, lifestyle adjustments and/or treatment of the underlying conditions related to GH deficiency might be sufficient to restore its’ levels without the need for supplementation.
For example, a malfunctioning thyroid is proven to interfere with the production and release of HGH by the liver. Correcting the thyroid dysfunction through other means may be all that is needed for HGH levels to rebound. In other cases of “primary” HGH deficiency – for example, in genetically-triggered deficiencies– the only viable treatment modality is to augment the insufficient endogenous HGH supply through supplementation.
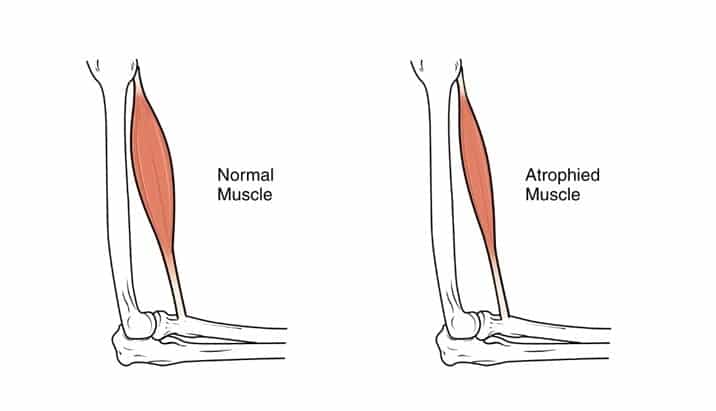
Sarcopenia
“Sarcopenia” is the medical term to refer to the muscle loss that commonly occurs in the elderly as a part of the aging process. Preliminary research on HGH and its protective effects on muscle and bone health in older populations is extremely promising.
An illustrative representation of sarcopenia in older adults. Therapy holds significant promise as an emerging treatment for the condition.
HGH Supplements in the General Public
The majority of HGH therapy patients in the modern era are otherwise healthy adults who have an easily corrected HGH deficiency. For this group, HGH is highly effective at restoring GH concentrations in the blood to ideal levels. The bottom line on the efficacy of therapy: in most cases, it carries a high risk-reward ratio. Your capability to safely receive HGH supplements depends on individual health markers that your doctor will investigate before initiating treatment.
Are HGH Supplements Truly Compatible With the Human Endocrine System?
Recombinant Human Growth Hormone (rHGH), frequently referred to as “somatropin,” is the active ingredient in most HGH supplement formulations. Somatropin has been shown to be highly bioactive, meaning that it works in the body the way it is intended to by binding to growth hormone receptor sites in cells. In effect, recombinant HGH acts just like the endogenous HGH that is produced naturally in the liver.
Is HGH Supplementation Really Safe?
Of course, no medical procedure is completely free of risk. The hazard level of HGH restoration depends heavily on the health status of the patient. Several biomarkers might raise red flags with a clinician prior to beginning therapy. Due to the extensive research on long-term dosing with exogenous HGH in humans, we know that even years-long regular administration of HGH does not trigger adverse reactions in most people. Although most of the studies focus on youths, we can reasonably extrapolate the effects of those studies to be relatively sure that it is comparably safe for adults.
A comprehensive blood screening is required for each patient before HGH supplementation to detect any potential health threats.
While the literature indicates that therapy is safe for the majority of patients, there are important caveats to consider regarding potential risk. Knowledgeable HRT doctors screen their patients for risk factors that might adversely influence the outcome of their HGH supplementation. Blood tests, in addition to measuring blood concentrations of GH itself, can inform the risk level for an individual patient.
For example, due to HGH’s substantial influence on metabolic processes, patients with blood markers for insulin resistance may be at a greater risk than others of developing diabetes following supplementation. Until a blood analysis is performed prior to treatment, determining risk on a case-by-case basis is impossible.
Risks Associated with Therapy
Because growth hormone acts on both the nervous and immune systems, it exerts a wide range of effects when introduced through supplementation. Again, the relative risks of hormone replacement therapy with HGH depend on individual risk factors. The general risks of GH therapy for various body systems are enumerated in the chart below.
| Patient Data | Benefits | Risks of Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Body Composition | Reduction in fat mass Increase in lean mass Increase in muscle strength |
Increase in BMI Increased waist circumference Increase of waist-hip index |
| Bone Metabolism | Increase in bone mineral density | Effect on the incidence of fractures not clearly shown |
| Health-related quality of life | Improvement in quality of life questionnaires Greater benefit in patients with low quality of life at baseline |
No improvement in all dimensions Probable absence of effect in patients with normal quality of life |
| Cardiovascular risk markers | Increase in HDL-chol Reduction of total and LDL-chol Diastolic blood pressure reduction Reduction of CRP Reduction of carotid intima-media thickness |
Reduced insulin sensitivity Increase in fasting glucose and insulin Trend to the increase in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome Increase in lipoprotein |
| Cardiovascular disease | Reduction in the incidence rate of myocardial infarction | Trend to increase cerebrovascular disease |
| Neoplasms | No increase in the rate of recurrence or progression of hypothalamic-pituitary tumors No increase in overall risk of neoplasia in adults with GHD |
Tendency to increase risk of second malignancy in childhood cancer survivors treated with GH in childhood There are subgroups with increased risk of certain neoplasia in adults who were treated with GH in childhood |
| Mortality | Tendency to decrease the global and cardiovascular mortality of hypopituitarism | Persistence of higher mortality than the general population in some studies |
During the consultation at a hormone replacement clinic, your doctor will perform a thorough physical evaluation to determine your personal risk factors to consider.
Research-Backed Conclusion: Is GH Supplementation the “Real Deal?”
By now, we have mountains of evidence from clinical studies that — in most cases of HGH deficiency — supplementation plays an integral role in the restoration of the endocrine system to optimal function. As we explored previously, HGH injection remains the most effective, proven technique for the safe yield of higher plasma GH concentrations. Patients typically notice positive results within a month of beginning treatment.
When selecting a doctor, always prioritize qualifications and experience. A qualified HGH doctor will perform a thorough physical exam and blood analysis to determine a patient’s fitness to safely receive replacement therapy. Visiting a reputable clinic will also guarantee that the HGH supplements used in your treatment are sourced from quality-ensured manufacturers. If you are experiencing any health issues associated with a decline in HGH levels, you could be a good candidate for replacement therapy. Contact your doctor today to get started with the evaluation process.